Coils wound into a spiral shape have inductance, which are used for electrical purposes and are called inductors. Inductors are widely used in power supplies and filtering circuits, which can be divided into two categories: inductors used for signal systems and power inductors used for power systems.
Inductors are also very common and are
easily overlooked for their basic parameters, resulting in inadequate design
and serious use issues for products. The more detailed things are, the more
worth pondering over, which is the basic skill of a hardware engineer. Figure
1-14 is the symbol of inductor components and the internal structure of
inductors, which can be divided into winding and stacking. Stacked inductors
have smaller volume, which is conducive to the miniaturization of circuits, so
they are widely used. The following introduces the basic parameters of
inductors.
 |
| Figure 1-14 Several common inductors |
1. Inductance value:
The basic
parameter of inductors and a key parameter affecting the ripple current of
power supply. Inductance and capacitance are complementary components and have
the most basic formula (1-2):
The current flowing through the power inductor in the DC-DC BUCK buck converter is a triangular wave current . As long as the conditions of the DC-DC converter are determined, the appropriate power inductor can be roughly calculated according to formula (1-3), where Vin is the input voltage, Vout is the output voltage, Fsw is the switching frequency, and Iout is the output current .
In the SPEC (also called datasheet,
specification or data manual) of the DC-DC converter, different inductance
values are recommended for use as reference. Therefore, many engineers do not
calculate, but only select according to the reference values of the
manufacturer. This does not achieve the best design in terms of performance and
price. This is because the recommended value in the manual is a general design
recommended by the power IC manufacturer. We need to optimize the inductor
selection based on the supplier's recommendation and the specific power
requirements of the load in our own products, so as to achieve the best circuit
design for our own products. Detailed introduction of inductor selection will
be introduced in later chapters.
2. Saturation current ISAT:
Also known as
DC superposition characteristics, which affects the effective inductance when
the inductor works. If the selection is not appropriate, the inductor will be
saturated, causing the actual inductance to decrease and not meet the design
requirements, or even cause the circuit to be burned. The definition of
saturation current varies from manufacturer to manufacturer. Generally, it
refers to the current when the initial inductance decreases by 30%. For
example, a 4.7 uH inductor decreases to about 3.3 uH when it is 1.5A (see
Figure 1-15). Note: If ISAT is not enough, the power supply ripple current will
increase with the decrease of inductance value, because according to formula
(1-3), when the load voltage Vout is unchanged, L decreases, Iout naturally
becomes larger, Iout increases will further reduce the inductance, which is a
dangerous thing.
 |
| Figure 1-15 Inductor saturation current |
3. Temperature rise current Itemp:
The
parameter specifying the allowable temperature range when using inductors (see
Figure 1-16). The definition of temperature rise current varies from
manufacturer to manufacturer. Generally, it refers to the current when the
inductor temperature rises by 30 ° C.
 |
| Figure 1-16 Inductor temperature rise current |
4. DC impedance RDC:
The resistance value
when passing DC, which affects the heat loss. Generally, the smaller the DC
resistance, the less the loss. Reducing RDC is slightly conflicting with
conditions such as size miniaturization (the smaller the inductance, the larger
the volume).
5. Impedance frequency characteristic:
The
ideal inductance impedance increases with frequency, that is, "through
straight gap exchange", but the actual inductance impedance decreases with
frequency due to parasitic capacitance and resistance, as shown in Figure 1-17.
This frequency is called the crossover frequency or resonance frequency, which is
similar to capacitance.
These are the characteristics of inductors.
When selecting inductors, be sure to carefully evaluate each parameter.
 |
| Figure 1-17 Actual inductance equivalent model and impedance-frequency curve |
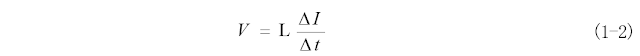

Comments
Post a Comment